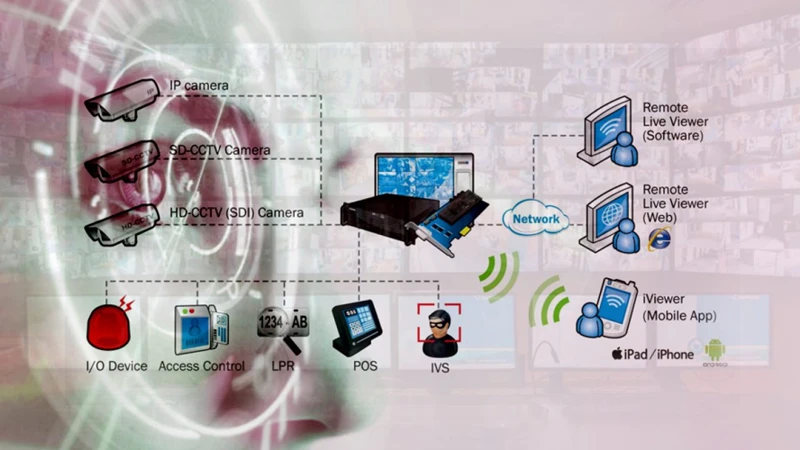
In today’s world, security is paramount, and businesses and organizations are constantly looking for innovative ways to enhance their surveillance systems. One such advancement is the integration of video surveillance with biometric identification technology. This powerful combination offers a more robust and secure solution for monitoring and controlling access to sensitive areas. In this guide, we will explore the benefits of integrating video surveillance with biometric identification and provide a comprehensive overview of how to implement this cutting-edge technology.
Benefits of Video Surveillance Biometric Identification
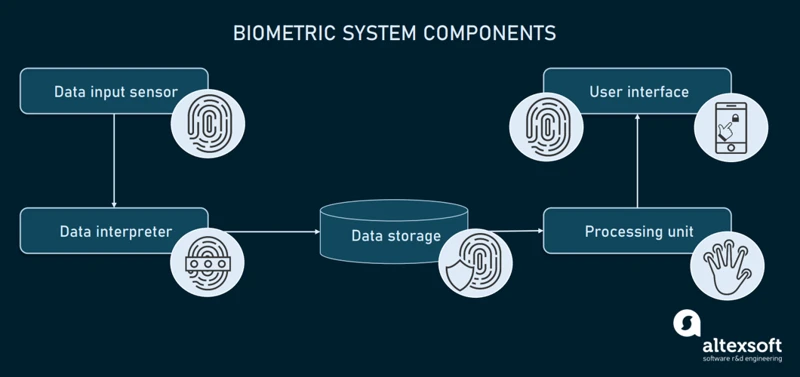
The integration of video surveillance with biometric identification brings a plethora of benefits to organizations across various industries. One of the key advantages is the enhanced security it provides. Traditional access control methods such as key cards or passwords can be easily compromised, but biometric identification adds an extra layer of security by using unique physical characteristics like fingerprints, facial recognition, or iris scans for authentication.
Moreover, the combination of biometrics with video surveillance allows for real-time monitoring and alerts. Security personnel can receive instant notifications when unauthorized individuals try to access restricted areas, enabling swift action to be taken to prevent security breaches. This proactive approach helps in reducing response times and improving overall security measures.
Another benefit of integrating video surveillance with biometric identification is the ability to create detailed audit trails. Every access attempt is logged and recorded, providing a comprehensive overview of who accessed specific areas and at what times. This information can be invaluable for investigations and compliance purposes, helping organizations maintain a secure and accountable environment.
Furthermore, the integration of these technologies can improve operational efficiency. By automating the authentication process, organizations can streamline access control procedures and reduce the burden on security personnel. This not only saves time but also minimizes the risk of human error in identifying individuals, leading to a more reliable and efficient security system.
Choosing the Right Biometric Identification Technology
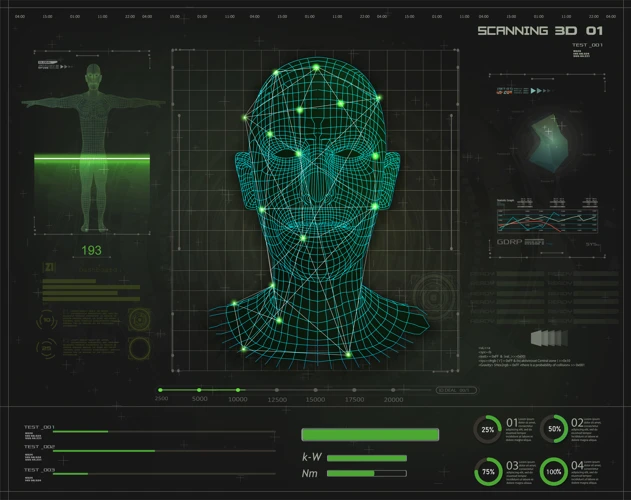
When it comes to integrating biometric identification with video surveillance, choosing the right technology is crucial for the success of the implementation. There are several biometric modalities available, each with its own strengths and limitations. Here are some key factors to consider when selecting biometric identification technology:
Accuracy and Reliability
One of the primary considerations when choosing biometric technology is its accuracy and reliability. Different modalities such as fingerprint recognition, facial recognition, iris scanning, and voice recognition vary in their accuracy rates and susceptibility to false positives and negatives. It is essential to evaluate the performance of each modality under various conditions and choose the one that best fits the organization’s security requirements.
Scalability and Integration
Scalability and integration capabilities are also crucial factors to consider. The chosen biometric technology should be scalable to accommodate future growth and changes in the organization’s security needs. Additionally, it should seamlessly integrate with existing video surveillance systems and access control infrastructure to ensure a smooth and efficient operation.
Compliance and Data Security
In today’s regulatory landscape, data security and compliance are paramount. Organizations must ensure that the biometric identification technology they choose complies with relevant privacy regulations and safeguards sensitive biometric data from unauthorized access. Encryption, data anonymization, and secure storage practices should be integral components of the chosen technology to protect personal information and maintain regulatory compliance.
User Experience
The user experience is another critical aspect to consider when implementing biometric identification technology. The system should be user-friendly, intuitive, and non-intrusive to ensure seamless authentication processes for employees, visitors, or customers. A positive user experience not only enhances security but also promotes user adoption and acceptance of the technology.
Implementation Guide

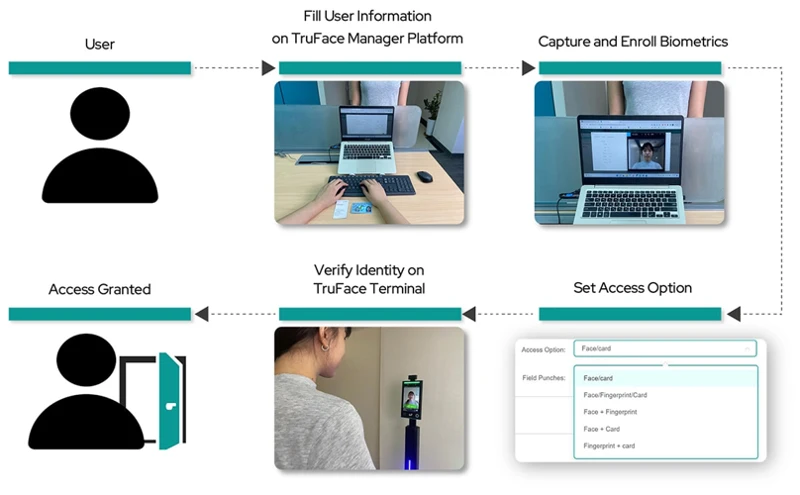
Once the right biometric identification technology has been selected, the next step is the implementation process. Here is a step-by-step guide to integrating video surveillance with biometric identification:
Assessment and Planning
Before starting the implementation, conduct a thorough assessment of the organization’s security needs, existing infrastructure, and budget constraints. Identify key access points that require biometric identification and determine the number of users who will be enrolled in the system. Develop a comprehensive implementation plan that outlines the deployment strategy, timeline, and resource requirements.
Hardware and Software Installation
Acquire the necessary hardware components such as biometric scanners, cameras, servers, and access control panels. Install the hardware in strategic locations based on the assessment conducted earlier. Configure the software applications for biometric enrollment, authentication, and integration with the video surveillance system. Test the hardware and software components to ensure they are functioning correctly and communicating effectively with each other.
Enrollment and User Training
Enroll authorized users into the biometric identification system by capturing their biometric data and linking it to their user profiles. Provide comprehensive training to users on how to use the biometric scanners, follow authentication procedures, and understand the importance of maintaining security protocols. Encourage users to ask questions and provide feedback to address any concerns or issues during the training process.
Integration and Testing
Integrate the biometric identification system with the video surveillance infrastructure to enable real-time monitoring and alerts. Configure the system to generate notifications for unauthorized access attempts, tampering with devices, or system malfunctions. Conduct thorough testing of the integrated system to ensure all components are functioning correctly, and security protocols are being enforced as intended.
Monitoring and Maintenance
After the implementation is complete, establish a monitoring and maintenance schedule to ensure the system remains operational and secure. Regularly review audit logs, access reports, and system alerts to identify any anomalies or security breaches. Perform routine maintenance tasks such as software updates, hardware inspections, and user database management to keep the system running smoothly and efficiently.
Looking to enhance your video surveillance system with advanced features? Check out our articles on installing video surveillance systems, video analytics for evidence gathering, integrating remote monitoring in video surveillance, tips for home surveillance camera placement, and understanding different video storage options to take your security setup to the next level!
Conclusion
The integration of video surveillance with biometric identification technology offers a powerful solution for enhancing security and access control in organizations. By leveraging the benefits of biometric authentication combined with real-time monitoring capabilities, businesses can create a more secure environment and improve operational efficiency. Choosing the right biometric technology, following a structured implementation process, and prioritizing user experience and data security are essential steps in successfully integrating video surveillance with biometric identification. With the right approach and careful planning, organizations can leverage this advanced technology to strengthen their security posture and protect their assets effectively.